Abstract
Recent research in language-guided visual navigation has demonstrated a significant demand for the diversity of traversable environments and the quantity of supervision for training generalizable agents. To tackle the common data scarcity issue in existing vision-and-language navigation datasets, we propose an effective paradigm for generating large-scale data for learning, which applies 1200+ photo-realistic environments from HM3D and Gibson datasets and synthesizes 4.9 million instruction-trajectory pairs using fully-accessible resources on the web. Importantly, we investigate the influence of each component in this paradigm on the agent's performance and study how to adequately apply the augmented data to pre-train and fine-tune an agent. Thanks to our large-scale dataset, the performance of an existing agent can be pushed up (+11% absolute with regard to previous SoTA) to a significantly new best of 80% single-run success rate on the R2R test split by simple imitation learning. The long-lasting generalization gap between navigating in seen and unseen environments is also reduced to less than 1% (versus 8% in the previous best method). Moreover, our paradigm also facilitates different models to achieve new state-of-the-art navigation results on CVDN, REVERIE, and R2R in continuous environments.
Video
SoTA Timeline
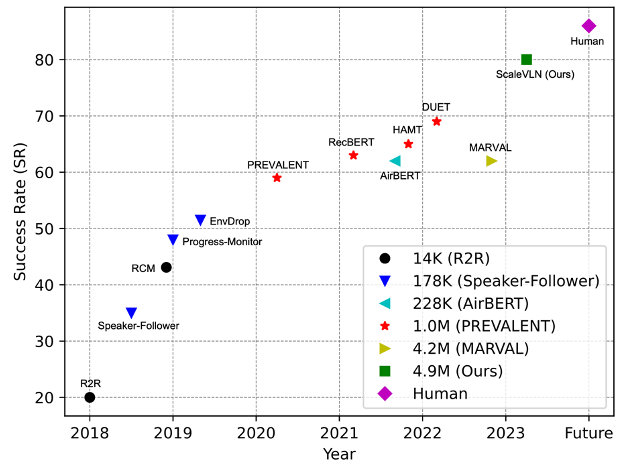
Agent success rate with increasing data size on addressing the R2R navigation task over time. Our proposed method creates 4.9M instruction-trajectories pairs for learning, which greatly boosts the agent’s performance, and for the first time approaching human results.
Overview
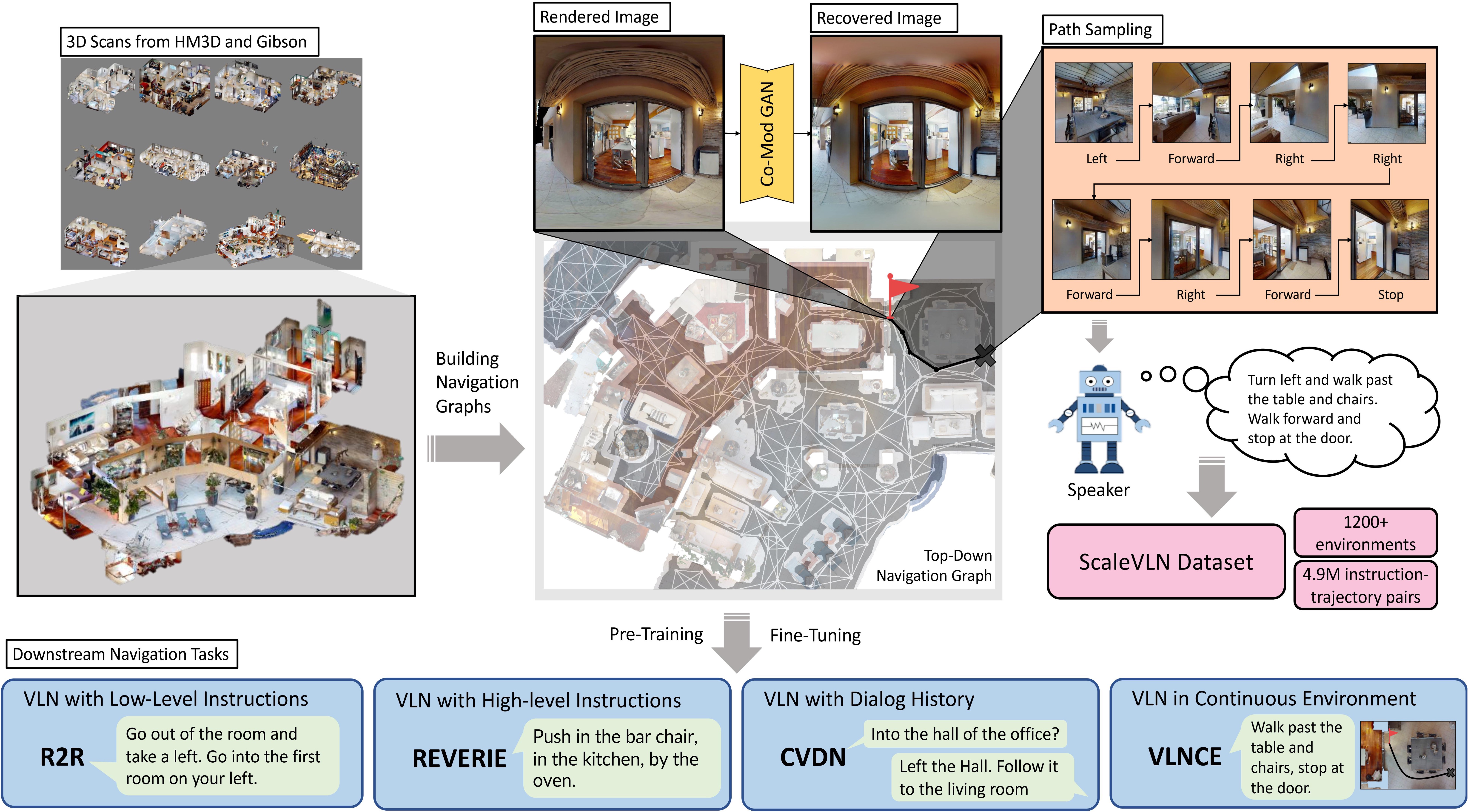
Overview of our ScaleVLN paradigm for generating large-scale augmented VLN data. ScaleVLN applies 1200+ unannotated 3D scans from the HM3D and Gibson environments, builds navigation graphs for each scene, recovers faulty rendered images with a Co-Mod GAN, samples trajectories and generates corresponding instructions, resulting in 4.9M augmented data to facilitate learning various downstream language-guided navigation tasks.
How to utilize the ScaleVLN data?
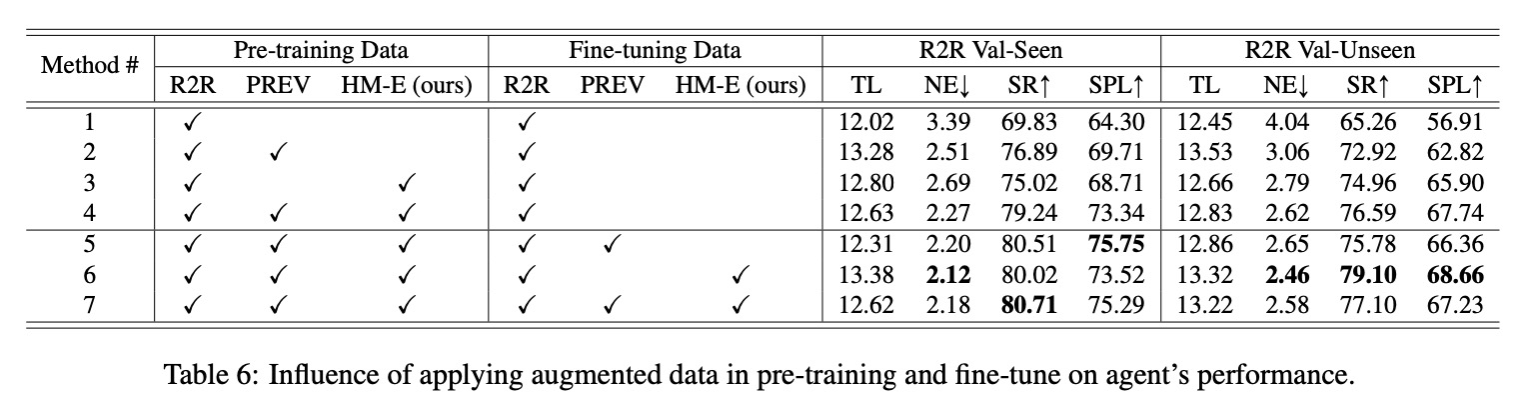
We found that incorporating with ScaleVLN data always improves agent performances while pretraining with Prevalent and ScaleVLN, then finetuning with only ScaleVLN as augmentation datasets performs best.
Results
Bridging the Seen-and-Unseen Gap
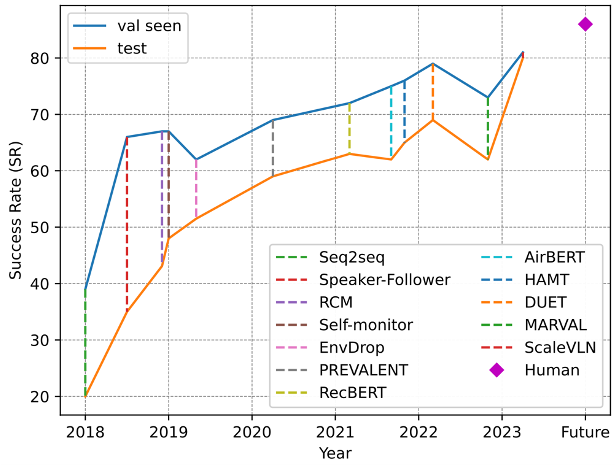
Comparison to SoTA
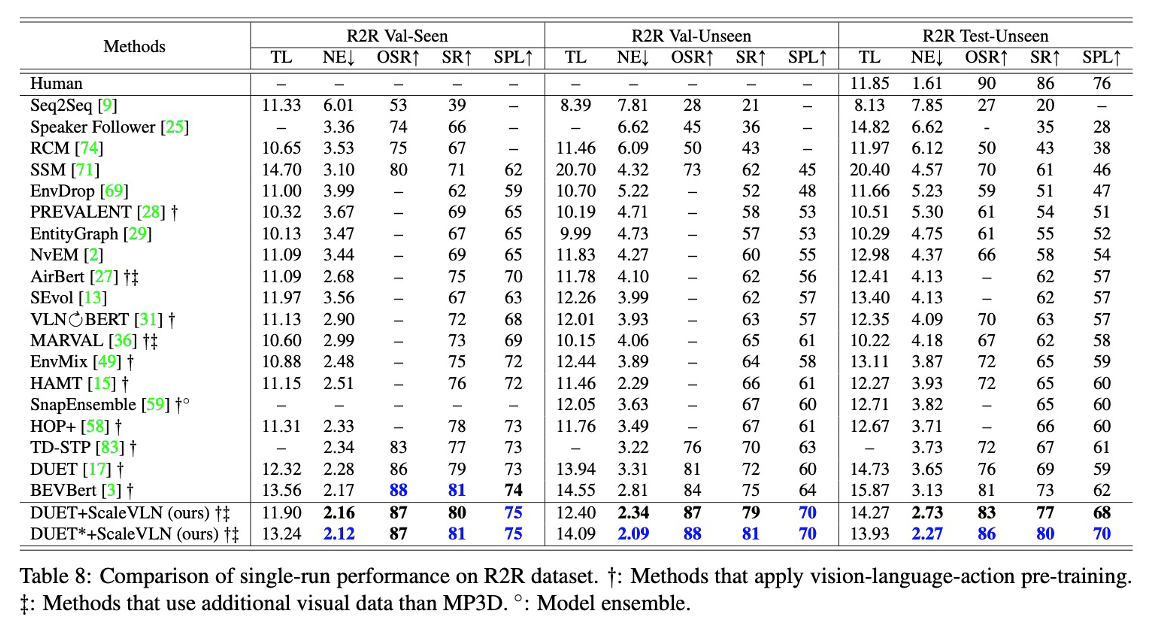
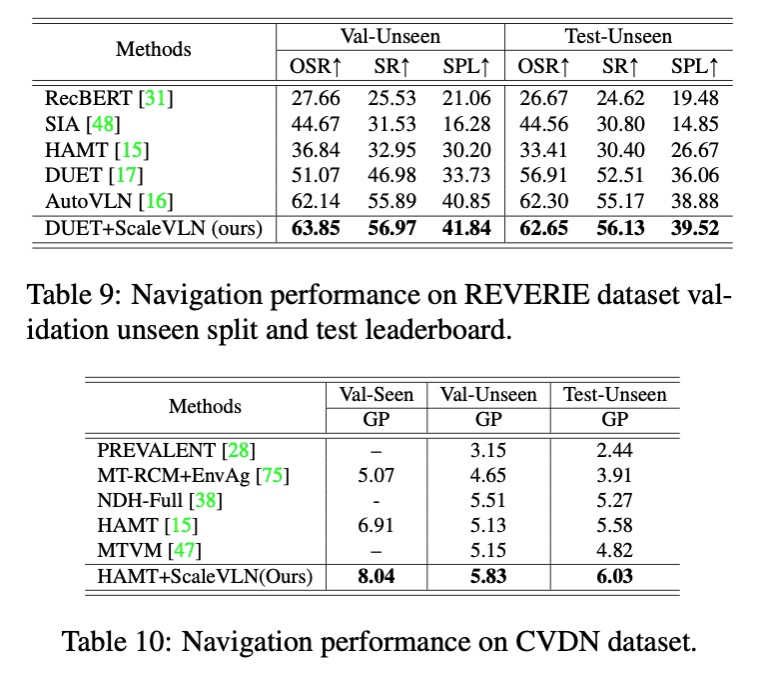
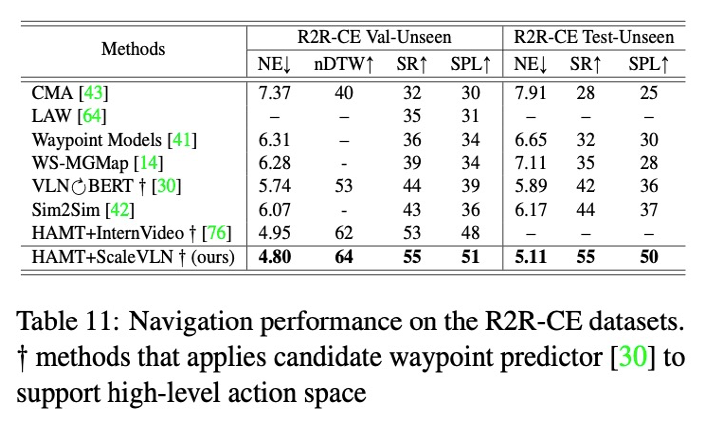
Comparison with state-of-the-art agents on Room-to-Room (R2R), REVERIE, Cooperative Vision-and-Dialog Navigation (CVDN), and Room-to-Room in Continuous Environment (R2R-CE) datasets.
Scaling VLN data, What Really Matters?
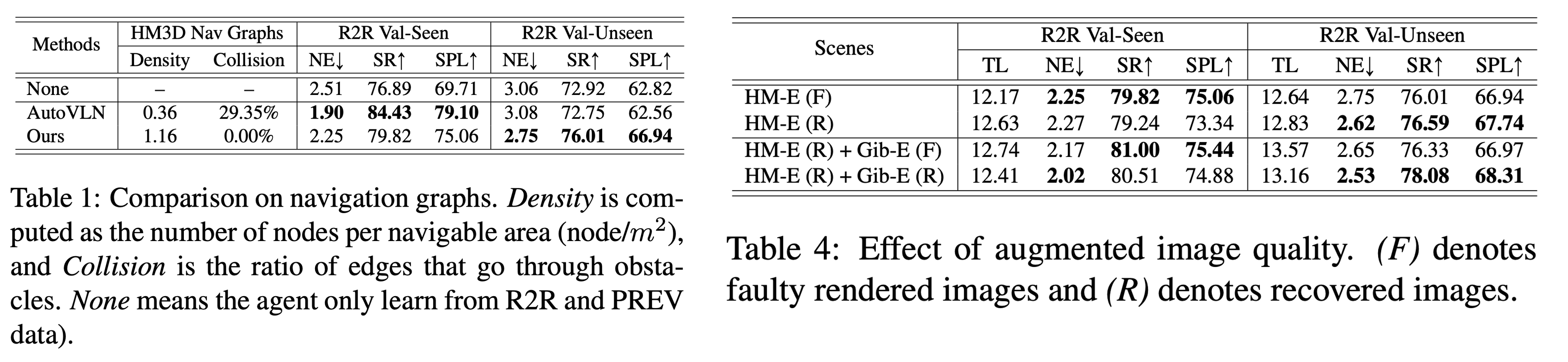
We show that traversable graphs and photorealistic images improve downstream performance.
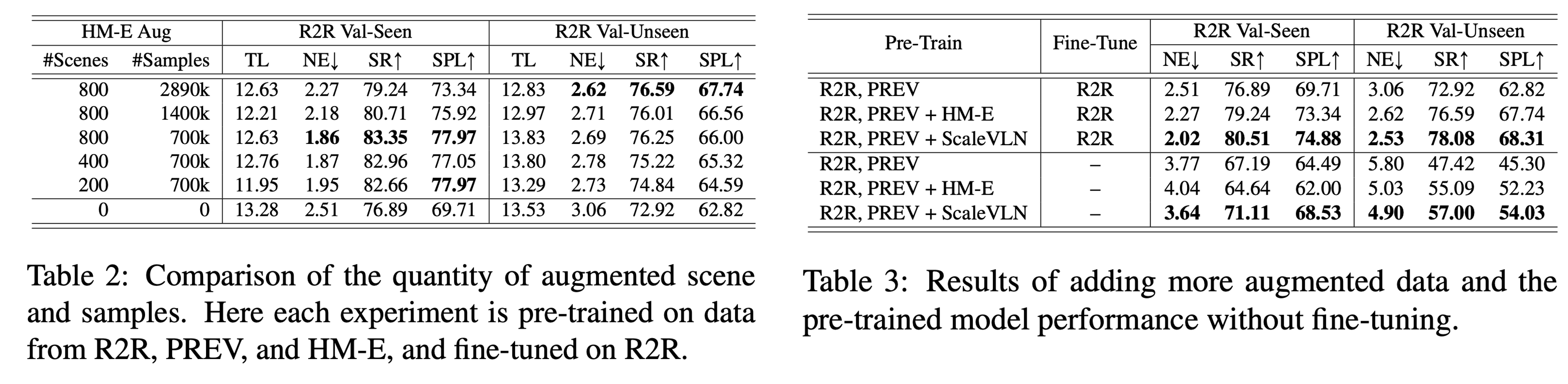
We show that adding more scenes and data consistently improves downstream performance.
BibTeX
@InProceedings{wang2023scalevln,
author = {Zun Wang, Jialu Li, Yicong Hong, Yi Wang, Qi Wu, Mohit Bansal, Stephen Gould, Hao Tan, Yu Qiao},
title = {Scaling Data Generation in Vision-and-Language Navigation},
booktitle = {ICCV 2023},
year = {2023}
}